In the world of injection molding, understanding the differences between hot runner and cold runner systems is crucial. These systems play a pivotal role in determining the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of your production process. Hot runner systems maintain the plastic in a molten state, allowing for faster cycle times and reduced waste. In contrast, cold runner systems let the plastic cool and solidify, which can lead to increased material waste but offer simplicity and lower initial costs. Choosing the right system depends on your specific application needs, production volume, and budget considerations.
Understanding Hot Runner Systems
In the realm of injection molding, hot runner systems play a crucial role in enhancing production efficiency. These systems maintain the plastic in a molten state throughout the molding process, ensuring that the material flows smoothly into the mold cavities without solidifying prematurely.
How Hot Runner Systems Work
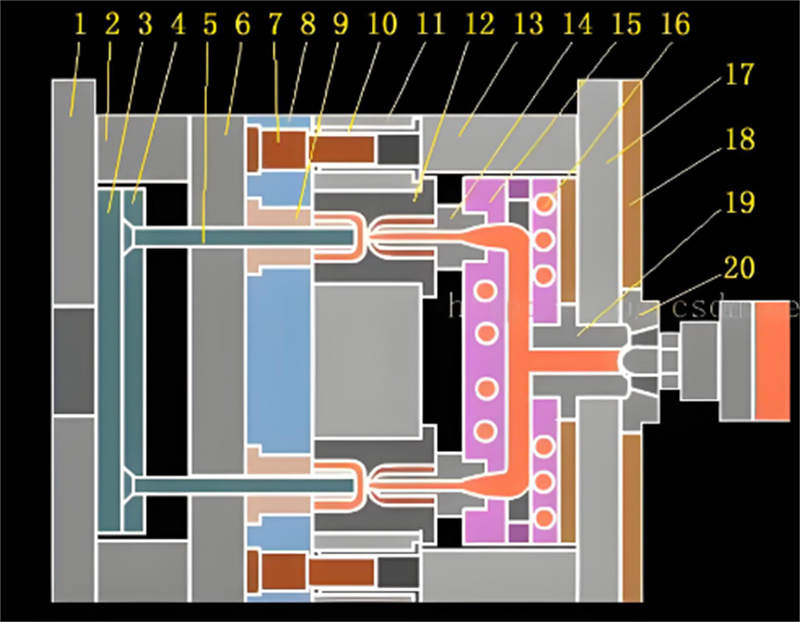
A hot runner system operates by using heated components to keep the plastic material in a liquid state. This system comprises several key components:
Components of Hot Runner Systems
- Heated Barrel: This component keeps the plastic hot and ready for injection.
- Manifold: It distributes the molten plastic evenly to various nozzles.
- Nozzles: These guide the plastic directly into the mold cavities.
These components work together to ensure that the plastic remains molten until it fills the mold cavities completely.
Gating Methods in Hot Runner Systems
The gating methods in hot runner systems are essential for controlling the flow of plastic into the mold. These methods include:
- Externally Heated Gates: Suitable for heat-sensitive materials, providing precise control over the flow.
- Internally Heated Gates: Offer better flow control, ideal for complex geometries.
Advantages of Hot Runner Systems
Choosing a hot runner system offers several benefits:
Reduced Waste and Material Costs
By eliminating solid runners, hot runner systems significantly reduce material waste. This reduction leads to lower material costs and a more sustainable production process.
Improved Cycle Times and Efficiency
With the plastic remaining molten, hot runner systems enable faster cycle times. This efficiency boosts overall production speed, making them ideal for high-volume manufacturing.
Disadvantages of Hot Runner Systems
Despite their advantages, hot runner systems have some drawbacks:
Higher Initial Costs
The initial investment for a hot runner system is higher compared to cold runner systems. This cost includes the advanced technology and components required to maintain the plastic in a molten state.
Maintenance and Complexity
Hot runner systems require regular maintenance due to their complexity. The intricate components and temperature controls demand careful attention to ensure optimal performance.
Exploring Cold Runner Systems
Cold runner systems offer a different approach in injection molding. They allow the plastic to cool and solidify within the runner system before reaching the mold cavities. This method can be more suitable for certain applications, especially when considering cost and simplicity.
How Cold Runner Systems Operate
Cold runner systems function by channeling the molten plastic through unheated runners. As the plastic travels, it cools and solidifies, forming a runner that must be removed after the molding process.
Components of Cold Runner Systems
- Sprue: Connects the injection unit to the runner system.
- Runners: Channels that guide the plastic to the mold cavities.
- Gates: Control the flow of plastic into the mold.
These components work together to ensure the plastic reaches the mold cavities, albeit in a solidified form.
Types of Cold Runner Molds
Cold runner molds come in various types, each suited for different applications:
- Two-Plate Molds: Simple design, ideal for basic parts.
- Three-Plate Molds: Offer more flexibility in part design and gating.
Advantages of Cold Runner Systems
Cold runner systems provide several benefits that make them appealing for specific scenarios:
Lower Initial Costs
Cold runner systems typically require a lower initial investment. The absence of complex heating elements reduces the upfront costs, making them more accessible for small-scale production.
Simplicity and Ease of Maintenance
The straightforward design of cold runner systems simplifies maintenance. You can easily manage and repair these systems without the need for specialized knowledge or tools.
Disadvantages of Cold Runner Systems
Despite their advantages, cold runner systems have some drawbacks:
Increased Material Waste
Cold runner systems generate more material waste. The solidified runners must be trimmed and discarded, leading to higher material costs over time.
Longer Cycle Times
The cooling and solidification process in cold runner systems results in longer cycle times. This can slow down production, making them less efficient for high-volume manufacturing.
Choosing the Right System for Your Needs
Selecting between hot runner and cold runner systems requires careful consideration of various factors. Each system offers unique benefits and challenges, and your choice should align with your specific production needs and goals.
Factors to Consider
Production Volume and Cost
When deciding on a system, consider the production volume. Hot runner systems often justify their higher initial costs with long-term savings in material waste and cycle times. If you plan to produce large volumes, the efficiency of a hot runner system can offset its upfront expenses. On the other hand, cold runner systems might be more suitable for smaller production runs due to their lower initial investment.
Material and Part Design
The complexity of your part design and the materials you use also influence your decision. Hot runner systems excel with complex parts, offering better flow control and reducing quality issues. They also provide greater design flexibility and material compatibility. For simpler designs or when using materials that do not require precise temperature control, cold runner systems can be a practical choice.
Application Suitability
Industry-Specific Considerations
Different industries have varying requirements that can affect your choice. For instance, industries focusing on high production efficiency and complex parts may benefit more from hot runner systems. Conversely, industries that prioritize cost-effectiveness and simplicity might lean towards cold runner systems.
Environmental Impact
Consider the environmental impact of each system. Hot runner systems reduce material waste by eliminating solid runners, which contributes to a more sustainable production process. Cold runner systems, while simpler, generate more waste due to the need to trim and discard solidified runners. If sustainability is a priority, the reduced waste of a hot runner system might be more appealing.
By evaluating these factors, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your production goals and industry requirements.
In summary, hot runner and cold runner systems offer distinct advantages and challenges in injection molding. Hot runner systems enhance production speed and part quality by maintaining plastic in a molten state, reducing defects like sink marks. Cold runner systems, however, provide cost benefits and simplicity. Align your choice with your business needs and application requirements. Consider both short-term and long-term implications. A hot runner system may require a higher initial investment but can lead to increased efficiency and output rates, making it a valuable option for high-volume production.
