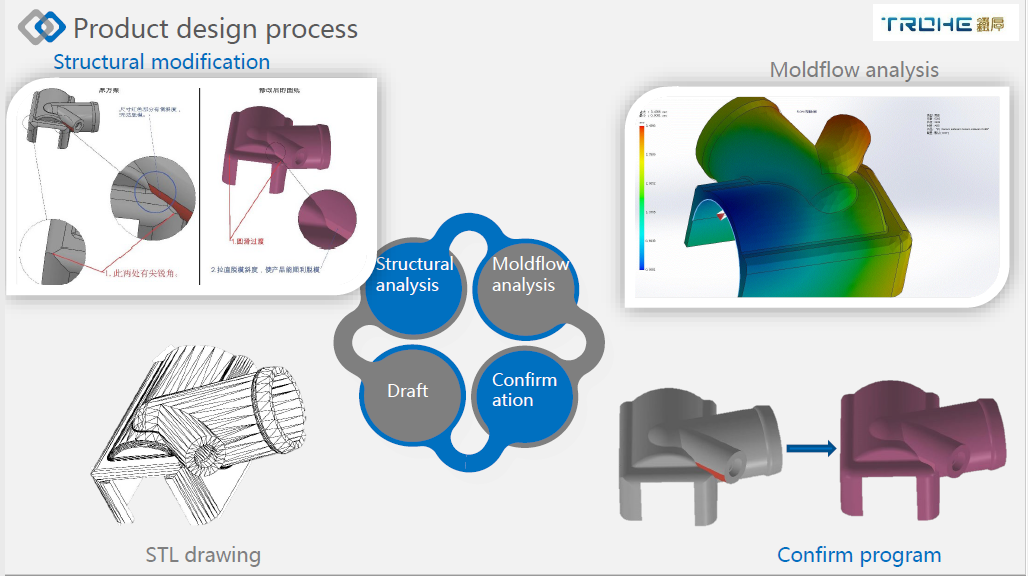
- Design: Begin with conceptualization and CAD modeling.
- Prototype: Rapid prototyping and iteration.
- Design for Manufacturability: Material selection and process optimization.
- Tooling: Mold design and tool fabrication.
- Sampling: Initial production run and quality assurance.
- Production: Full-scale manufacturing and continuous improvement.
Quality control ensures product integrity, reduces defects, and improves cost efficiency. As the plastics market grows, mastering these steps becomes even more vital.
Design
Conceptualization
Understanding the product requirements and specifications is the first step in the design phase of Plastic Parts Manufacturing. You need to gather all necessary information about the product’s intended use, environment, and performance expectations. This understanding forms the foundation for your design process. Once you have a clear picture of what the product needs to achieve, you can begin with initial sketches and design ideas. These sketches serve as a visual representation of your concepts, allowing you to explore different possibilities and refine your ideas before moving on to more detailed work.
CAD Modeling
After conceptualization, you transition to creating detailed 3D models using CAD software. This step is crucial because it transforms your initial sketches into precise digital representations. CAD drawings provide a comprehensive view of the design, showcasing every detail in either 2D or 3D format. They act as a blueprint for the mold to be built, ensuring that every aspect of the design is accounted for. When preparing for a CAD drawing, selecting the right program is essential. Popular choices include SolidWorks and AutoCAD, each offering unique features suited for different design needs. Consulting an expert can help you navigate these options effectively.
Ensuring design accuracy and feasibility is paramount during this stage. You must verify that the model aligns with the product requirements and can be manufactured efficiently. This involves checking dimensions, tolerances, and material compatibility. By doing so, you minimize potential issues during production and enhance the overall quality of the final product.
Prototype
Rapid Prototyping
In the realm of Plastic Parts Manufacturing, rapid prototyping stands as a pivotal step. You utilize technologies like 3D printing to create quick prototypes. This approach allows you to transform digital designs into tangible models swiftly. By doing so, you can test design concepts and functionality without delay.
Expert Testimony:
EngineeringGuides highlights that rapid prototyping involves techniques to quickly fabricate a physical part from a three-dimensional design. This method enables engineers and designers to iterate between digital designs and physical prototypes efficiently.
Rapid prototyping offers a cost-effective workflow. You can make adjustments instantly, which elevates the trial and error process. This flexibility ensures that you refine your designs to achieve a better final product.
Iteration and Feedback
After creating prototypes, gathering feedback becomes essential. You engage stakeholders to evaluate the prototypes. Their insights help you identify areas for improvement. This collaborative approach ensures that the design aligns with user expectations and requirements.
Once you collect feedback, you make necessary design adjustments. This iterative process is crucial in refining the product. By continuously improving the design, you enhance its functionality and appeal.
Expert Testimony:
Design is inherently iterative, requiring multiple rounds of testing and refinement. Rapid prototyping with 3D printing provides the flexibility to implement changes swiftly, as noted by industry experts.
Through iteration and feedback, you ensure that the final product meets the highest standards of quality and performance.
Design for Manufacturability
Material Selection
Choosing the right plastic materials is a critical step in Plastic Parts Manufacturing. You must consider several factors to ensure the material fits the part’s requirements. First, evaluate the application and functionality of the part. Ask yourself what the part will do and where it will be used. This helps you determine the necessary performance attributes, such as strength, flexibility, or resistance to environmental conditions.
Next, think about the aesthetics and dimensional accuracy. Some applications demand a specific look or precise measurements. You should also weigh the durability of the material. Will the part need to withstand wear and tear over time? Finally, consider cost-effectiveness. Many users opt for cost-effective materials, especially for prototypes that do not require enhanced mechanical properties. This approach saves money while still allowing you to test and refine your designs.
Process Optimization
Once you select the material, focus on optimizing the design for manufacturing processes. Ensure that your design is suitable for the chosen manufacturing method. This involves simplifying the design to reduce complexity. A less complex design minimizes potential production issues and enhances efficiency.
You should also aim to streamline the manufacturing process. Look for ways to eliminate unnecessary steps or features that complicate production. By doing so, you not only save time but also reduce costs. This optimization ensures that the manufacturing process runs smoothly, resulting in high-quality parts.
Tip: Regularly review and refine your design to adapt to new technologies and methods. This proactive approach keeps your manufacturing process efficient and up-to-date.
Tooling
Mold Design
Designing molds is a crucial step in Plastic Parts Manufacturing. You need to focus on creating molds that ensure efficient production. Start by specifying the size, shape, and material of the mold. This precision is vital because any errors can lead to financial losses and wasted time. Proper mold design minimizes distortions in the final parts, ensuring they meet the desired specifications.
Consider factors like mold flow and cooling during the design process. Mold flow refers to how the molten plastic moves through the mold. You must ensure that the flow is smooth and even to avoid defects. Cooling is equally important. It affects the cycle time and quality of the molded parts. Efficient cooling systems reduce production time and improve part quality.
Tip: Pay attention to wall thickness in your mold design. Uniform wall thickness helps in achieving consistent quality and reduces the risk of warping.
Tool Fabrication
Once you finalize the mold design, move on to tool fabrication. This involves creating the physical molds using precision machining. You must ensure that the molds are crafted with high accuracy. Precision machining allows you to achieve the exact dimensions and features required for the mold.
Testing molds for accuracy and durability is essential. Conduct thorough inspections to verify that the molds meet the design specifications. Durability testing ensures that the molds can withstand repeated use without degrading. This step is crucial for maintaining consistent quality in mass production.
Advice: Regular maintenance of molds extends their lifespan and ensures consistent performance. Schedule routine checks to identify and address any wear or damage.
Sampling
Initial Production Run
In the Plastic Parts Manufacturing process, you begin with an initial production run. This step involves producing a small batch of parts. The purpose is to test and evaluate these parts before full-scale production. You focus on assessing the quality and consistency of the parts. This evaluation helps you identify any potential issues early. By doing so, you can make necessary adjustments to improve the final product.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance plays a vital role in ensuring the success of your manufacturing process. You conduct thorough inspections and tests on the initial batch of parts. These inspections help you verify that the parts meet the required standards and specifications. Testing includes checking for defects, measuring dimensions, and evaluating material properties.
Based on the test results, you make adjustments to the manufacturing process. This might involve tweaking the design, altering the material, or refining the production technique. By addressing these issues early, you enhance the overall quality of the final product. This proactive approach ensures that the parts you produce meet the highest standards of excellence.
Production
Full-Scale Manufacturing
In the realm of Plastic Parts Manufacturing, scaling up production becomes essential to meet growing demand. You must transition from small batches to full-scale manufacturing efficiently. This step requires careful planning and resource allocation. You need to ensure that your production line can handle increased volume without compromising quality.
Consistent quality and efficiency are paramount during this phase. You should implement robust quality control measures to maintain high standards. Regular inspections and testing help identify any deviations early. By doing so, you prevent defects and ensure that every part meets the required specifications. Efficiency in production not only saves time but also reduces costs, enhancing overall profitability.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is a key aspect of successful Plastic Parts Manufacturing. Implementing feedback loops allows you to gather insights from various stages of production. You should actively seek feedback from operators, engineers, and customers. This information helps you identify areas for enhancement and innovation.
Adapting to new technologies and methods is crucial for staying competitive. You should stay informed about the latest advancements in manufacturing techniques. Incorporating new tools and processes can improve efficiency and product quality. By embracing change and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, you ensure that your manufacturing process remains cutting-edge and effective.
In the journey of Plastic Parts Manufacturing, each step plays a vital role in ensuring high-quality outcomes. From design to production, you must pay attention to every detail. Properly implementing these steps guarantees that your final product meets quality, safety, and environmental standards. Quality control is not just a step but an integral part of the process. It ensures consistent quality and brings numerous benefits beyond the product level. As you embark on your manufacturing endeavors, consider these steps carefully to achieve excellence in your products